Energy Poverty Kills
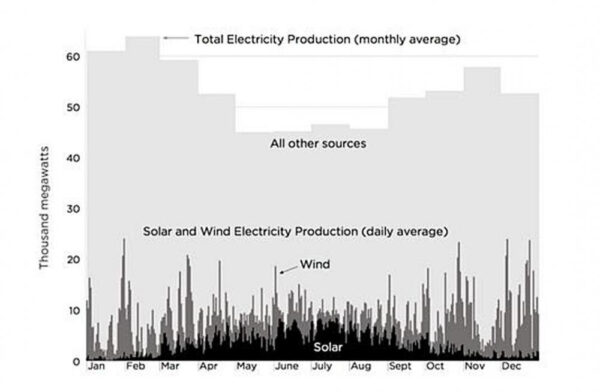
From Center for Industrial Progress by Alex Epstein Last week we looked at the need for a process of producing energy that is cheap, plentiful, and reliable—and we saw that solar and wind cannot produce cheap, reliable energy. How Germany embraced solar and wind and ended up in energy poverty Let’s take a look at this in practice. Germany is considered by some to be the best success story in the world of effective solar and wind use, and you’ll often hear that they get a large percentage of their energy from solar and wind. You can see here on this chart how this claim was made and why it’s not accurate. First of all, this is just a chart of electricity. Solar and wind are only producing electricity and half of Germany’s energy needs also include fuel and heating. So solar and wind never contribute half as much to Germany’s energy needs as this chart would imply. But that’s not the biggest problem. What you notice here is that there’s certain days and times where there are large spikes, but there are also periods where there’s relatively little. What that means is that you can’t rely on solar and wind ever. You always have to have an infrastructure that can produce all of your electricity independent of the solar and wind because you can always go a long period with very little solar and wind. So then why are the solar and wind necessary? Well, you could argue that they’re not and that adding them onto the grid will impose a lot of costs. In Germany, electricity prices have more than doubled since 2000 when solar and wind started receiving massive subsidies and favorable regulations, and their electricity prices are three to four times what we would pay in […]
Energy Poverty Kills Read More »