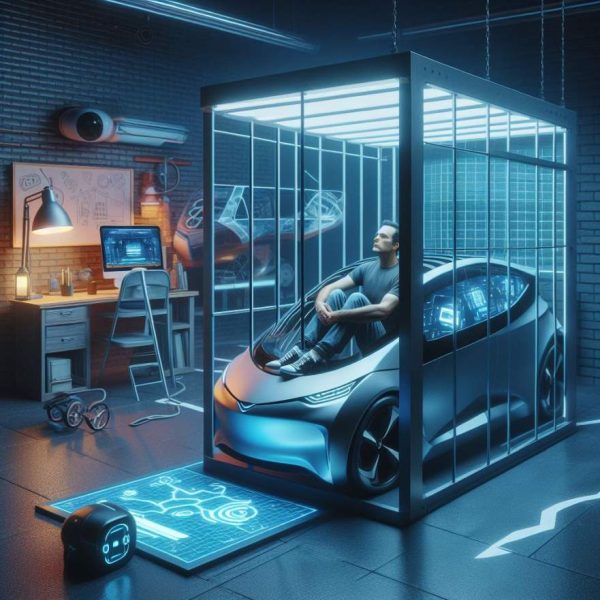
Electric Car Prison
Will electric cars lead you to incarceration? Find out….. An article by Dave Arthurwith illustration by Wayfarer The other day I was talking to someone who was thinking of buying an electric car. I told him he should first get to know a good bail bondsman and a lawyer. I told him that I am serious about this. You buy an electric car, you think you are helping the environment. You completely ignore the pollution caused from pit mining in order to get the materials to make the batteries. You also ignore the problems of disposing of these batteries in landfills or wherever once they are used up. Maybe you buy the electric car cause you want to save money by not buying gasoline. You ignore the fact that it still costs plenty of money to charge the batteries in these cars. Electricity is far from free. You also ignore the initial cost of these cars which is one third or more higher than a comparable gasoline powered mode. Maybe you think if you’re not buying gas you will soon recoup the difference. You weren’t too good at math. It might take eight or nine years to recoup that money in gas savings, but by then the car-battery will be no good anymore and you will need a new car. What about disposing the old one? So what does all that have to do with going to prison because you bought an electric car. CLICK HERE TO FIND OUT AND READ THIS ARTICLE ONLY ON BIKERNET.com
Electric Car Prison Read More »